AWS: Cloud Servers
Review, Research, and Discussion
- Describe the Web-Request-Response-Cycle
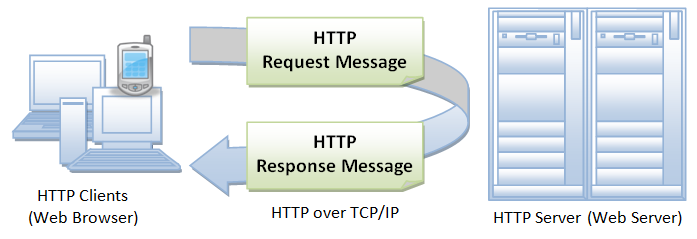
- Explain what a “server” is, as it relates to the WRRC
Once the client’s request has reached the server, the server will search for and return the information the client is requesting. Often times, this means querying a database, loading the information into an html page, and returning the HTML text to the user in the body of the HTTP response.
- What does it mean to “deploy” an application?
Document the following Vocabulary Terms
- Server: which responds (or serves) to the requests of the user-agent with information.
- Pub/Sub:Publish–subscribe pattern is a form of asynchronous service-to-service communication used in serverless and microservices architectures. In a pub/sub model, any message published to a topic is immediately received by all of the subscribers to the topic. Pub/sub messaging can be used to enable event-driven architectures, or to decouple applications in order to increase performance, reliability and scalability.
- WRRC: The process used by the Internet Transaction Server (ITS) to drive applications is similar in all Structure linkimplementation models.
Preparation Materials
What is a Virtual Machine (VM)? A virtual machine (VM) is a virtual environment that functions as a virtual computer system with its own CPU, memory, network interface, and storage, created on a physical hardware system (located off- or on-premises). Software called a hypervisor separates the machine’s resources from the hardware and provisions them appropriately so they can be used by the VM.
What Is a Hypervisor? The central component of a VM is a type of software;A hypervisor acts to isolate an individual virtual machine in the cloudspace. A hypervisor isn’t just a divider for your VMs — it’s much more than that. In addition to providing an impermeable virtual border between multiple OSes, your hypervisor will simulate the hardware components of a traditional operating system.
What Is Cloud Computing?
Virtualization : enables users to disjoint operating systems from the underlying hardware, i.e, users can run multiple operating systems such as Windows, Linux, on a single physical machine at the same time. Such operating systems are known as guest Oses (operating systems).
Github view
