growthmindsit
Trees
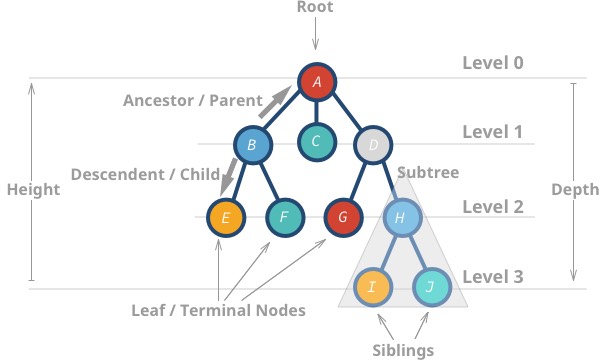
Common Terminology
- Node - A Tree node is a component which may contain it’s own values, and references to other nodes
- Root - The root is the node at the beginning of the tree
- K - A number that specifies the maximum number of children any node may have in a k-ary tree. In a binary tree, k = 2.
- Left - A reference to one child node, in a binary tree
- Right - A reference to the other child node, in a binary tree
- Edge - The edge in a tree is the link between a parent and child node
- Leaf - A leaf is a node that does not have any children
- Height - The height of a tree is the number of edges from the root to the furthest leaf.
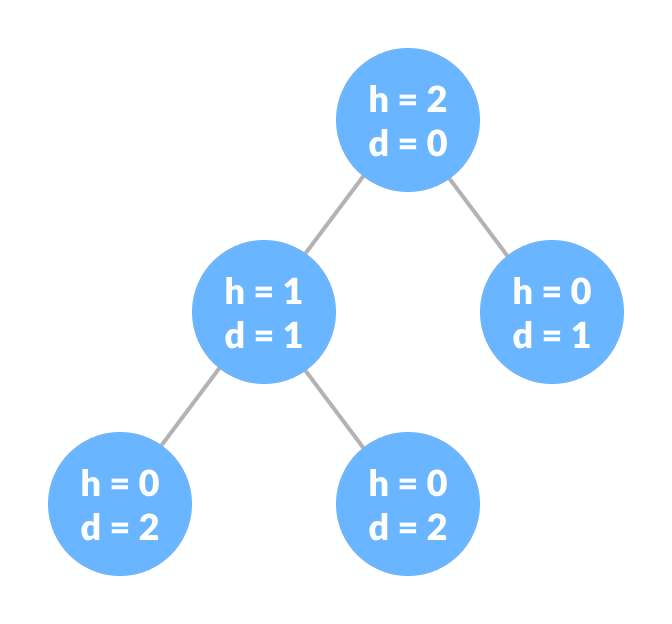
- Height of a Node : The height of a node is the number of edges from the node to the deepest leaf (ie. the longest path from the node to a leaf node).
- Depth of a Node : The depth of a node is the number of edges from the root to the node.
- Height of a Tree : The height of a Tree is the height of the root node or the depth of the deepest node.
A tree is a nonlinear hierarchical data structure that consists of nodes connected by edges.
Why Tree Data Structure?
Other data structures such as arrays, linked list, stack, and queue are linear data structures that store data sequentially. In order to perform any operation in a linear data structure, the time complexity increases with the increase in the data size. But, it is not acceptable in today’s computational world.Different tree data structures allow quicker and easier access to the data as it is a non-linear data structure.
Types of Tree:
- Binary Tree : A binary tree is a tree data structure in which each parent node can have at most two children.
Each node of a binary tree consists of three items:
-
data item
-
address of left child
- address of right child

- Binary Search Tree : Binary search tree is a data structure that quickly allows us to maintain a sorted list of numbers.
- It is called a binary tree because each tree node has a maximum of two children.
- It is called a search tree because it can be used to search for the presence of a number in O(log(n)) time.
The properties that separate a binary search tree from a regular binary tree is
- All nodes of left subtree are less than the root node
- All nodes of right subtree are more than the root node
-
Both subtrees of each node are also BSTs i.e. they have the above two properties
- K-ary Trees: The K-ary tree is a rooted tree, where each node can hold at most k number of children.If the value of k is 2, then this is known as binary tree. The binary tree, or ternary trees are some specialized k-ary trees. So k-ary trees re generalized.

Tree Traversal - inorder, preorder and postorder
raversing a tree allows us to search for a node, print out the contents of a tree, and much more! There are two categories of traversals when it comes to trees:
- Depth First
- Breadth First