Message Queues
Review, Research, and Discussion
- What does it mean that web sockets are bidirectional? Why is this useful?
it mean you can transfer the data from client to sever and from server to client so they allow real-time data transfer.
- Does socket.io use HTTP? Why?
Yes it’s use it but it doesn’t need an HTTP server to regular websockets,but it is used to allow HTTP and websocket servers to co-exist on the same TCP port.
- What happens when a client emits an event?
The event gets passed to the server through websockets. Its a tcp connection from the client to the server. The connection meaning the server can send real time data to the client and vise versa.
- What happens when a server emits an event?
will run the event in the client that was listinig for this event.
- What happens if a client “misses” an event?
The events will be ignored
- How can we mitigate this?
using queues
Document the following Vocabulary Terms
- Socket:is a software structure within a network node of a computer network that serves as an endpoint for sending and receiving data across the network.
- Web Socket: The WebSocket API is an advanced technology that makes it possible to open a two-way interactive communication session between the user’s browser and a server. With this API, you can send messages to a server and receive event-driven responses without having to poll the server for a reply.
- Socket.io :is a library that enables real-time, bidirectional and event-based communication between the browser and the server. It consists of:a Node.js server and Javascript client library for the browser (which can be also run from Node.js
- Client: is a computer or a program that, as part of its operation, relies on sending a request to another program or a computer hardware or software that accesses a service made available by a server
- Server:is a piece of computer hardware or software (computer program) that provides functionality for other programs or devices, called “clients”.
- OSI Model: (Open Systems Interconnection Model) is a conceptual framework used to describe the functions of a networking system.
- TCP Model:TCP model defines how devices should transmit data between them and enables communication over networks and large distances. The model represents how data is exchanged and organized over networks.
- TCP: stands for Transmission Control Protocol a communications standard that enables application programs and computing devices to exchange messages over a network.

- UDP: UDP (User Datagram Protocol) is a communications protocol that is primarily used for establishing low-latency and loss-tolerating connections between applications on the internet. It speeds up transmissions by enabling the transfer of data before an agreement is provided by the receiving party. As a result, UDP is beneficial in time-sensitive communications,
- Packets : is a small segment of a larger message. Data sent over computer networks*, such as the Internet, is divided into packets. These packets are then recombined by the computer or device that receives them.
Preparation Materials

Rooms and Namespaces
Rooms :is an arbitrary channel that sockets can join and leave. It can be used to broadcast events to a subset of clients:
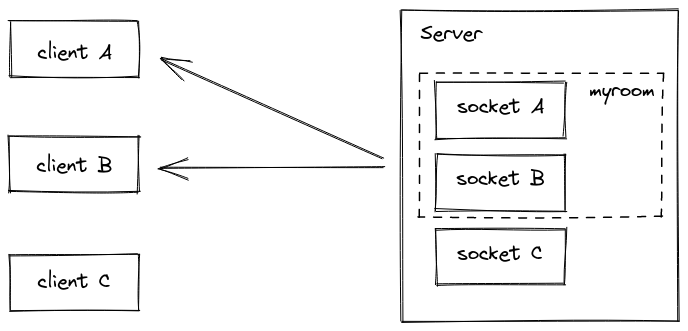
Please note that rooms are a server-only concept ( the client does not have access to the list of rooms it has joined).
With multiple Socket.IO servers Like global broadcasting, broadcasting to rooms also works with multiple Socket.IO servers.You just need to replace the default Adapter by the Redis Adapter.
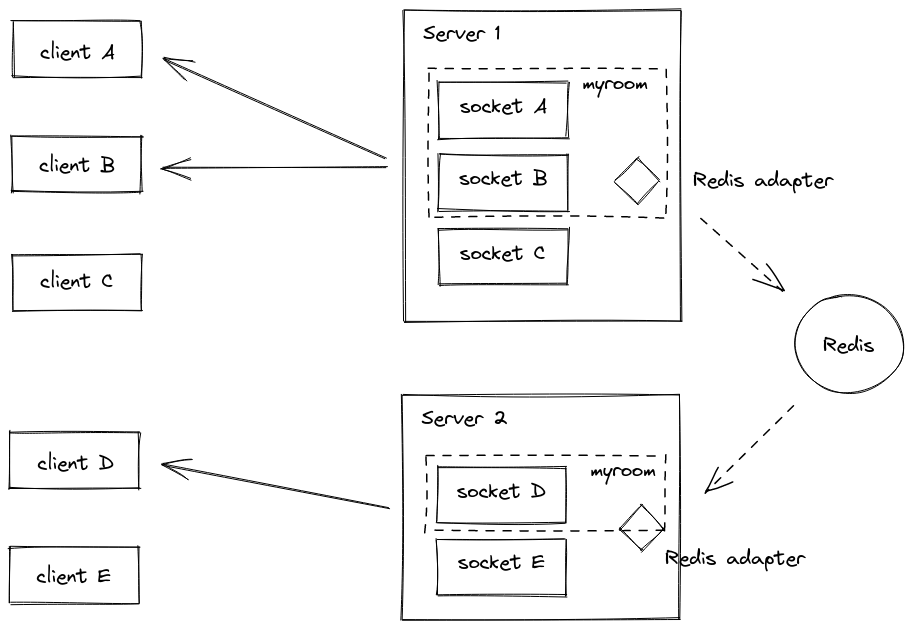
Room events : Starting with socket.io@3.1.0, the underlying Adapter will emit the following events:
- create-room (argument: room)
- delete-room (argument: room)
- join-room (argument: room, id)
- leave-room (argument: room, id)
Github view


